In May 2016, we detected a generic form grabber and IBAN (International Bank Account Number) swap script injection targeting financial institutions across the world. IBAN swapping is a technique fraudsters use to first obtain access to an account, then exchange a legitimate account number with the attacker’s destination mule account number before a funds transfer takes place.
In the process of identifying the script, our analysts discovered a target pattern of IBAN number formats that matched those of various countries in Europe and the Middle East. The script author also had been routinely upgrading the script injection content, including changes that blocked requests without correct referrers set in the request, hidden fields, and a keyboard simulation component designed to change values in the user page.
Targeted Country Patterns
The script target pattern matches the IBAN number formats for several countries such as Albania, Cyprus, Hungary, Lebanon, and Poland. Poland and Hungary share the exact IBAN number format matches, while Albania, Cyprus and Lebanon match because the bank identifiers are only numeric in those countries. For countries such as Azerbaijan and Guatemala, the format is the correct length, but because they use non-numeric bank identifiers, these countries do not match the pattern in the malicious script.
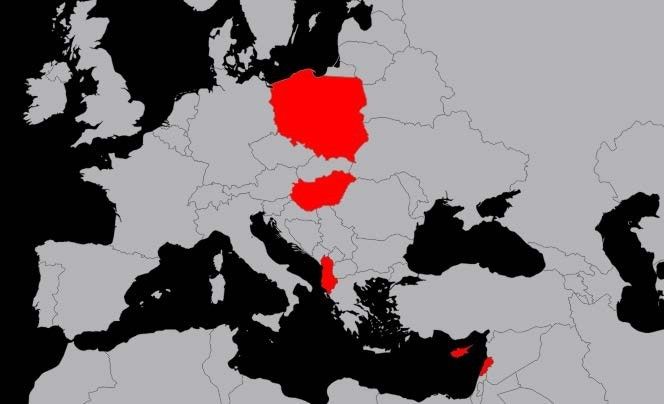
Figure 1: Countries attacked by the IBAN form grabber
Figure 1: Countries attacked by the IBAN form grabber
Fundamental Features of the Script
Attack URL: hxxps://googlapi.be/F2/00000123456789012345/1234567890.js
Attack IP Address: 213.167.241.238
The malicious script—just 41 lines of code in total—is a simple web injection designed to grab forms, and it uses regex to search for a specific pattern:

Figure 2: Conditional statement to identify a specific pattern of numbers
Figure 2: Conditional statement to identify a specific pattern of numbers
The data is sent by a function calling “new Image()” whenever a match for the pattern is detected. In the example below, you can see the stolen form data is sent as a URL. The data is encoded as part of the URL in a simple syntax, highlighted in yellow. The host name of the grabbed content is highlighted in red. Stolen input fields and non-essential form fields (submit, reset) are highlighted in green.

Figure 3: Stolen data in URL
Figure 3: Stolen data in URL
Script Updates Observed
Since detecting the first attack in May 2016, we have observed subsequent iterations of the attack server and the malicious script functionality. The first change was simple to identify because the server stopped responding to requests without referrers set in the request. This shows further malicious intent as the referrers are validated against an internal set of acceptable referrers. Referrers from general/non-financial sites or US-based financial sites do not yield the attack script.
Another change focused on adding a keyboard simulation component to alter values in the page, and additional hidden fields to store the originally entered IBAN. These new fields are sent along with the original form. The new IBAN field is injected as a hidden input field, and the original field is renamed and left visible so the victim is unaware of the change.

Figure 4: Dummy form with data submitted showing normal (uninfected) activity
Figure 4: Dummy form with data submitted showing normal (uninfected) activity

Figure 5: Dummy form with data submitted and IBAN swapped by keyboard simulator
Figure 5: Dummy form with data submitted and IBAN swapped by keyboard simulator
Detection Method
The format of the URL has been consistent throughout the attacks observed:
- The first folder is a single letter and a number. This is static, in our observation.
- A second folder is composed solely of numbers (15-20 digits in received alerts). The server responds to any numeric value of any length without any change to the returning file content.
- A filename is composed solely of numbers (10-15 digits) and has a .js file extension. The same behavior applies, with the server responding to any length and numeric value.
This attack has been observed on multiple domains and we have since set up alerts for what might possibly be the next domain.
Base URL | IP Address | Status |
https://googlapi.be/F3/ | 213.167.241.238 | Suspended |
https://natproxy.ws/C2/ | 94.242.232.12 | Suspended |
https://natrpoxy.ws/C3/ | 94.242.232.12 | Suspended |
https://nprixy.net/C2/ | Not resolving | Not active |
Figure 6: Summary of domain activities
Conclusion
The IBANs in question were reported to the appropriate financial institutions. The account was investigated, confirmed malicious, and was subsequently shut down.
Since we originally detected this web injection in May 2016, we have seen it change. Once valuable forms are identified, it is the next logical step for browser functionality to simulate the user entering other data in order to steal funds from accounts. This kind of behavior was documented in the "Slave" Malware Analysis Report (/content/f5-labs/en/labs/articles/threat-intelligence/slave-malware-analysis-evolving-from-iban-swaps-to-persistent-webinjects-22439.html) published in June 2015.1 We expect this attack to continue evolving into a complete Automatic Transfer System. This would enable attackers to initiate money transfers at will without them being intercepted. We are continuing to monitor the script’s behavior for changes and for any new related domains.