F5 Labs, in collaboration with Effluxio, researches global attack traffic to gain a better understanding of the cyberthreat landscape. Cyberattacks take many forms, but they often start with the hunt for exploitable services. This report analyzes scans of global low-interaction honeypots traps across three quarters of 2021, specifically comparing activity from the first two quarters, January through June, against the third quarter, July through September.
The connection attempts coming from these scans do not necessarily indicate malicious intent from a source country or organization. As this analysis shows, advanced attackers often make use of compromised infrastructure as proxy botnets. The country of origin of a vulnerability scan does not mean the hands on the keyboard are in that same country.
Highlights
- The top three scanned service ports in the first three quarters 2021 were all for remote logins, calling for hardening these services with patching and strong authentication.
- Malaysia saw a disproportionate amount of scanning traffic from an ASN assigned to Alibaba in China on MySQL port 3306 during Q3 2021.
- Lithuania was one of the top source countries for scans around the world during this period, but this is more likely Russian cyber-attackers hijacking Lithuanian infrastructure.
Top Scanned Ports
Since the Internet began, threat actors have scanned a wide range of IP ports to find potential targets. Each specific port represents certain potential services that can then be probed for vulnerabilities and exploited.
Top Targeted Services and Ports, Now and Then
Although threat actors probe many ports, so far in 2021 the top three scanned ports have remained the same. Those ports—5900 (VNC), 22 (SSH), and 3389 (RDP)—are all used for remote logins. However, all three declined slightly, with corresponding increases in scanning of ports 3306 (MySQL), 21 (FTP), and 9200 (Elasticsearch API). Figure 1 breaks down the specific proportions of the scanning traffic per port for the beginning and the latter half of 2021.
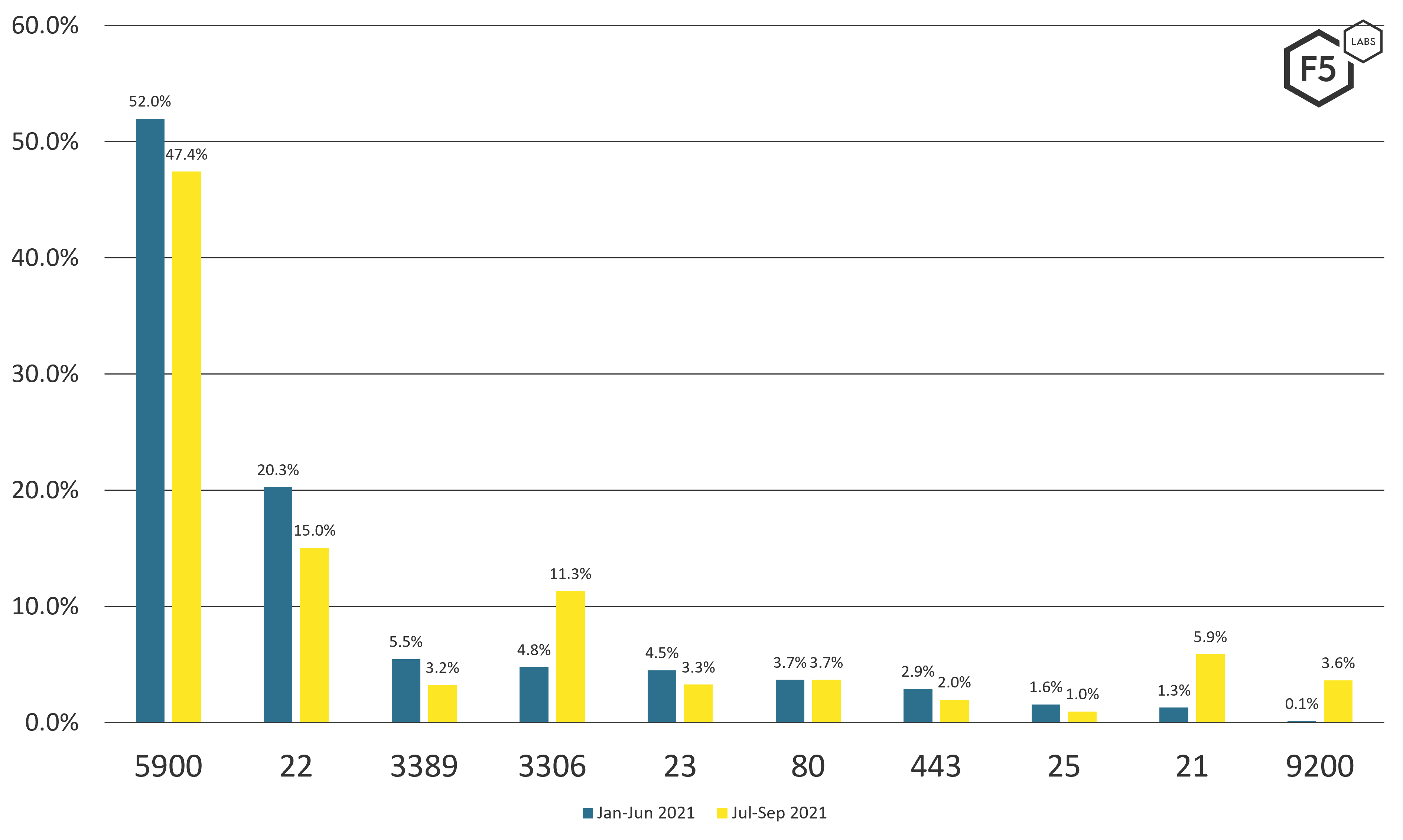
Figure 1. Attack traffic volumes targeting specific ports and services, January-June 2021 versus July-September 2021.
Remote Access Scanning
The top three global ports are used for remote administration and logins, meaning that a single successful authentication gives an attacker a direct login to an organization’s infrastructure. How commonly exposed are these ports? A search on Shodan shows nearly 5 million listening ports on 3389, over a million ports on 5900, and a whopping 21 million ports on 22.1
Given the prevalence of credential stuffing and phishing attacks, organizations opening these ports to the Internet should ensure they are patched and use strong authentication. System administrators, with their associated elevated privileges, should have even tougher controls in place for remote administration.
Port 9200 Scans in Third Quarter 2021
Taking a deeper dive into the increasing scans of port 9200, Elasticsearch listens on port 9200 and was in the top six globally for Q3 (3.6% of all scanning traffic). However, it was also in the top three for the United States in that same period, as shown in Figure 2. Why Elasticsearch? For one, it's been an unfortunate source of many large data breaches, as noted in the 2019 and 2021 Application Protection Reports. Based on this, F5 strongly recommends hardening all Internet-exposed APIs (/content/f5-labs-v2/en/archive-pages/education/securing-apis--10-best-practices-for-keeping-your-data-and-infra.html), especially heavily targeted APIs like Elasticsearch.
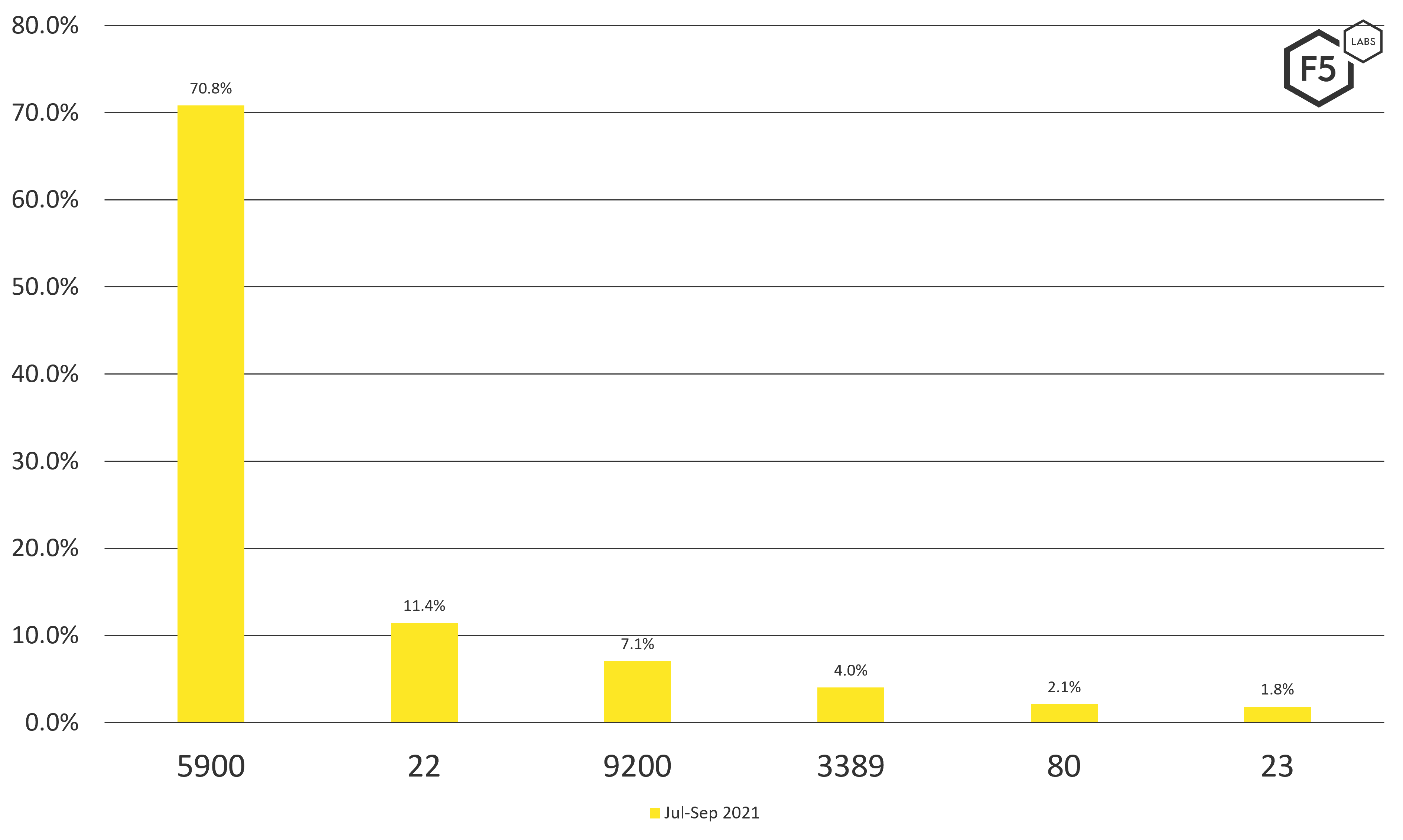
Figure 2. Top five scanned ports in the United States, July-September 2021.
Top Targets, Now and Then
The proportion of the four or so billion IP addresses on the Internet vary from country to country, based on usage and assignment. The exact breakdown of those assignments is easily referenced on Wikipedia (see Figure 3).2
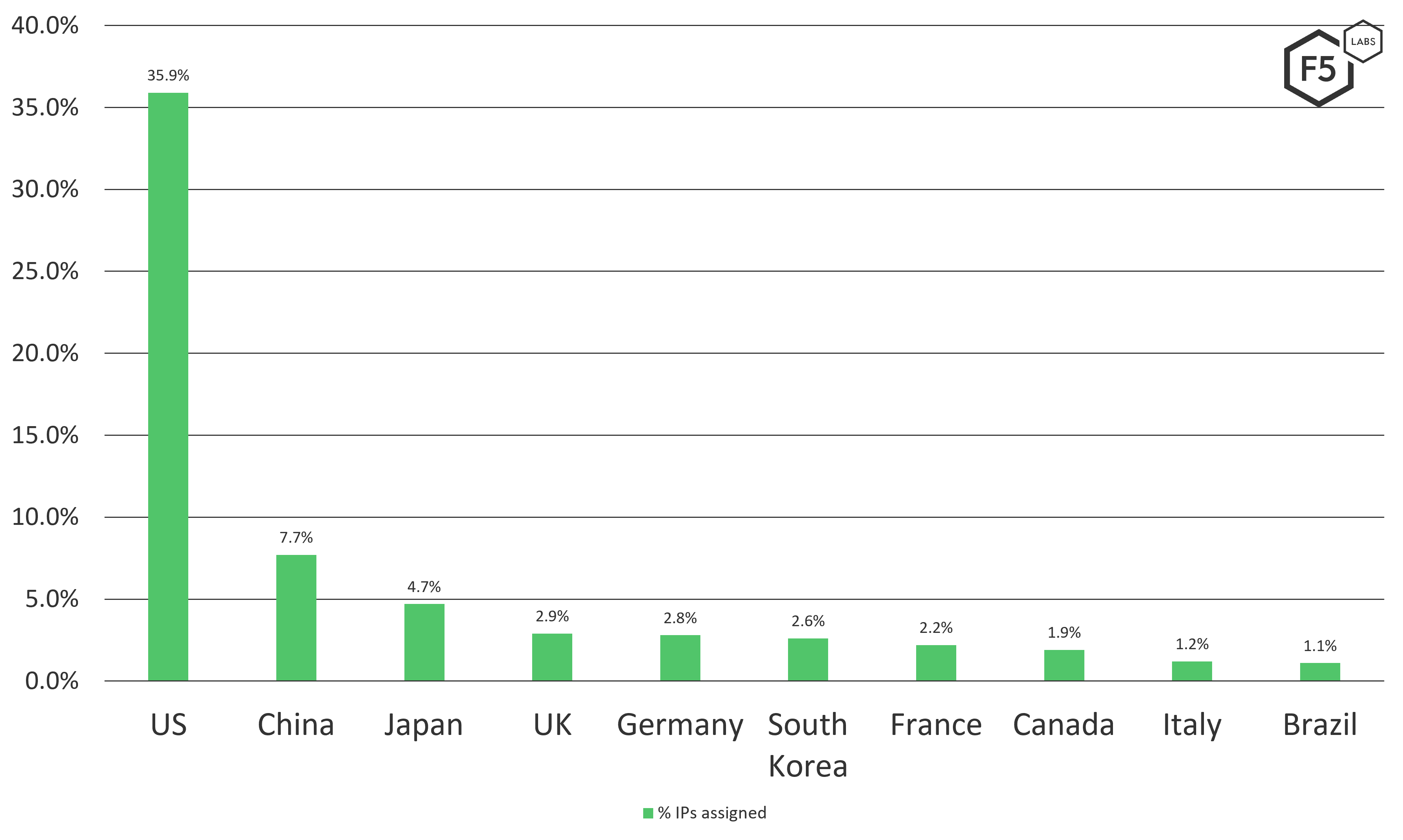
Figure 3. Top 10 assigned IP addresses per country.
All things being equal, the attacked countries seen in the Effluxio honeypot data should align somewhat with these same regional proportions. However, looking at the data, as shown in Figure 4, we can see this is not the case.
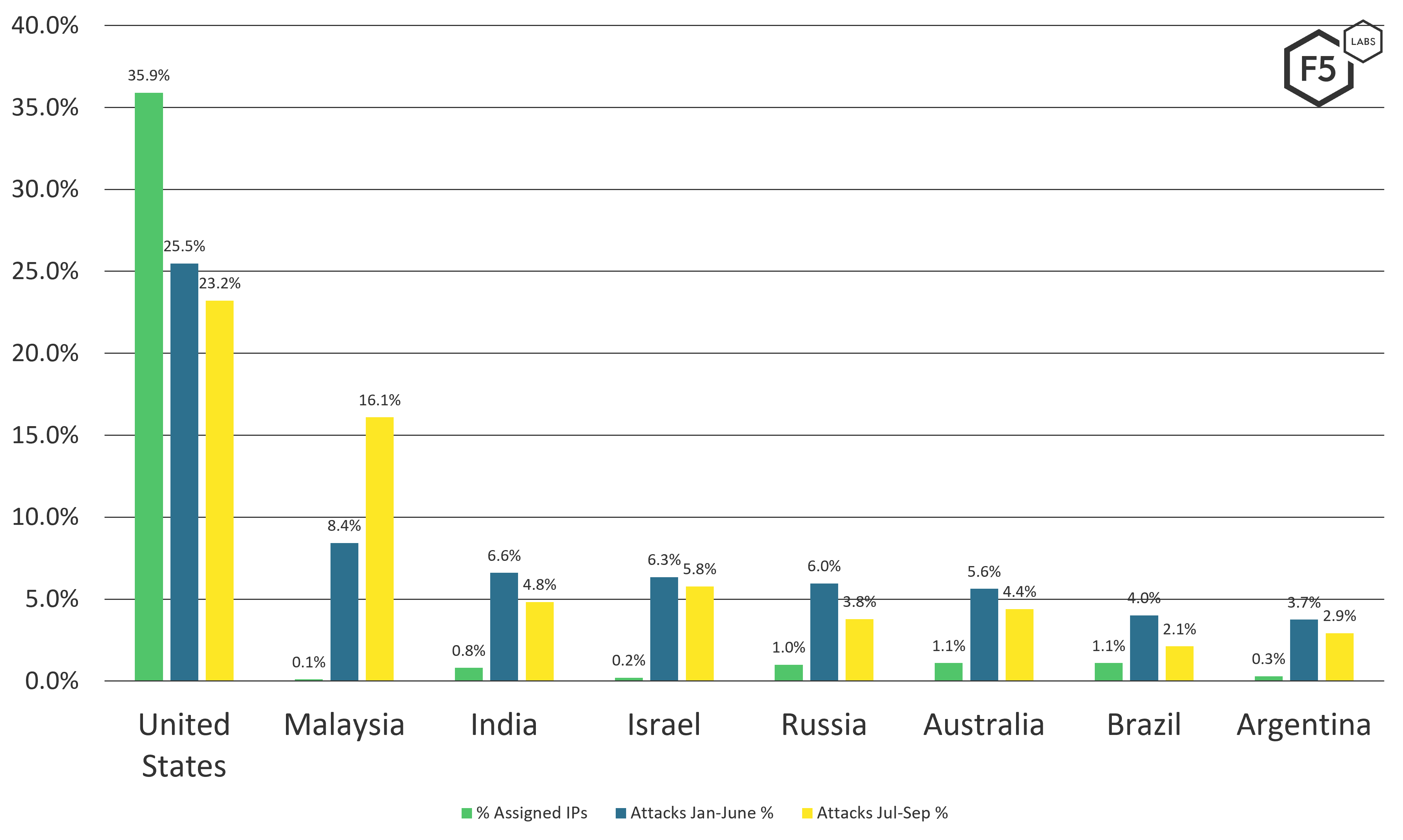
Figure 4. Attack traffic volume targeting specific countries, January-June 2021 versus July-September 2021.
Although the attack scan traffic into the United States is in line with the proportion of the assigned IP addresses, most of the other countries are not. The extreme outlier that stands out is Malaysia, rising to second place in Q3 2021.
Examining Attacks on Malaysia from China
Since this is so unusual, we examined attacks on Malaysia for July through September of 2021. The top three attacked ports in Malaysia were 3306 (79.53%), 5900 (14.31%), and 22 (3.83%). Nothing too out of bounds there, although it seems 3306 (MySQL) is seven times more targeted in Malaysia than it is globally (11.3%).
Inbound scans to Malaysia originated from China (20.52%), the United States (15.90%), Lithuania (9.21%), Germany (9.16%), and Russia (8.41%). Lithuania seems like an outlier here, but it actually is not out of line with the rest of the global attack traffic for the same period, which we will discuss shortly.
The actual outlier is China, which scanned Malaysia at nearly twice the level as it did on average across the Internet (11.2%). It looks like most of that traffic (20.83%) is coming from ASN 37963, which is assigned to Alibaba China. This is also out of proportion at nearly sixfold over the global average from that ASN (3.6%).
This could be just a particular discovery campaign by a cyber attacker using Alibaba scanners, or a statistical anomaly, or it could indicate a political change.3 We do not have enough data to determine anything beyond what we've reported here.
Who Is Scanning the Internet?
Let’s turn our attention to who is doing the scanning. Since we just dropped hints about Lithuania as a known outlier, let’s look at the top countries that originated scans to the lures. As with before, we’ll compare the beginning half of 2021 (January through June) and the third quarter (July through September). Figure 5 breaks down the top sources of scans.
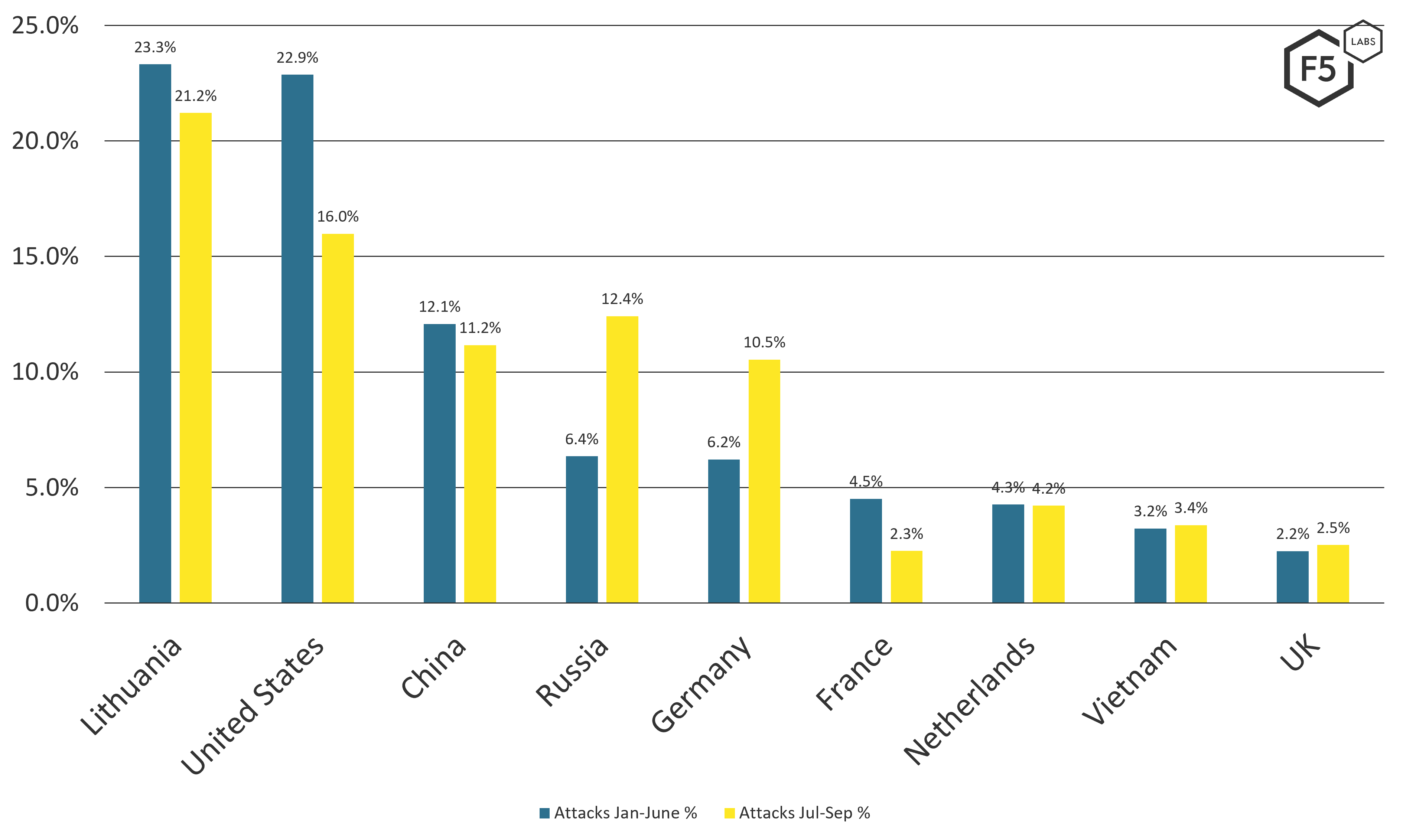
Figure 5. Top source countries for attack traffic, January-June 2021 versus July-September 2021.
The most unusual thing that stands out in the scan sources is Lithuania as the country of origin for the majority of cyberattack scans in 2021. Why is this happening? The answer comes from Lithuania’s State Security Department, which stated in March that Russian cyber attackers had been misusing its country’s IT infrastructure to attack other organizations developing COVID-19 vaccines.4 In fact, you can see the Lithuania-sourced traffic wane, presumably as it cleaned up the infections, while the Russia-sourced traffic rose again. However, this graph also hints that Germany may have a problem as well.
Top Source Organizations (ASNs) in 2021
The top ASNs stayed pretty much the same throughout 2021. Once again, we see Serverius Holding B.v. (AS50673) from the Netherlands at 33.8% and DigitalOcean (AS14061) at 10.3%. These have remained in the top for the past few years, so no surprises there.
Recommendations
- Prioritize hardening and patching for exposed ports that are commonly attacked, such as Elasticsearch APIs, VNC, and SSH.
- Enable multifactor authentication on every remote login service you can, implement a robust password policy on whatever you can't.
- Use an antibot solution to reduce brute force and credential stuffing attacks on logins.
- Use firewalls to restrict all unnecessary access to commonly attacked ports that must be publicly exposed.
- Disable weak and unused protocols, such as Telnet.
- Configure network access controls to only allow access to administrative ports from officially designated IP address ranges.